We have posted updates of the following topics:
Chemistry, toxicology & urinalysis > Management > Utilization management strategiesby Felix Leung, Ph.D.
Topic summary: Clinical laboratory has an essential role to maintain, audit and revise laboratory test ordering practices to ensure appropriate utilization. Laboratory utilization specifically focuses on ensuring that laboratory testing performed is aligned with the provision of high quality, cost effective patient care. Laboratory utilization initiatives commonly target tests that are ordered inappropriately or offer minimal value to patient management. Hard interventions: blocking repeating test orders, removing tests from menu, requiring approval for specific test orders, implementing reflexive testing algorithms; soft interventions: providing audit / feedback reports to clinicians, implementing automatic reminders within the test order system, disseminating educational material.
Chemistry, toxicology & urinalysis > Serology > Rheumatoid arthritis
by Lechuang Chen, Ph.D., Junyan Shi, Ph.D., Jieli (Shirley) Li, M.D., Ph.D.
Topic summary: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), classified as an autoimmune disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by joint swelling and tenderness, along with the progressive erosion of synovial joints; these symptoms often lead to significant disability and an increased risk of premature mortality. Although the etiology has not been identified, genetic factors play an important role, making family members of RA patients at higher risk. Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anticitrullinated protein / peptide antibodies (ACPA / anti-CCP), highly specific to RA, are key serological markers used in diagnosis. Patients treated effectively, especially when treated early with antirheumatic drugs, may exhibit a decrease in anti-CCP concentrations.
Lymphoma & related disorders > Mature B cell neoplasms > Large B cell lymphomas-special subtypes > Nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
by Jayalakshmi Balakrishna, M.D., Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D.
Topic summary: Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) is a B cell neoplasm characterized by scattered clonal cells (termed lymphocyte predominant [LP] cells) in a background of reactive lymphocytes and histiocytes, with a mostly nodular and sometimes diffuse growth pattern. LP cells initially arise within altered follicles; background small B cells are numerous in early phases and decrease with time. M:F = 3:1; median age at presentation is 30 – 40 years. Usually presents as localized disease; usually stage I / II (70 – 80%); 20% may present with advanced stage disease. Excellent prognosis; remission rate of 90 – 100% after primary therapy and overall 10 year survival rates > 90% in limited stage disease.
Skin nontumor > Alopecia > Dissecting cellulitis
by Pooria Zare, M.D., M.P.H., Mazaher Ramezani, M.D.
Topic summary: A neutrophilic scarring alopecia and member of follicular occlusion tetrad with the same histopathology. Fluctuating nodules on scalp, including occiput and vertex, leading to sinus tract formation. Pathophysiology: obstruction of the follicle with keratin plug, resulting in secondary rupture and inflammation. Mainly found in young males of African ancestry but can affect any age and race. Etiology not completely understood; genetic and hormonal factors. Diagnosis: physical examination and trichoscopy; skin biopsy. Nodules wax and wane but untreated disease results in scarring alopecia. Treatment: retinoids, systemic antibiotics, electron beam radiation, 800 nm pulsed diode laser, TNFα inhibitors, surgical intervention.
Featured Image
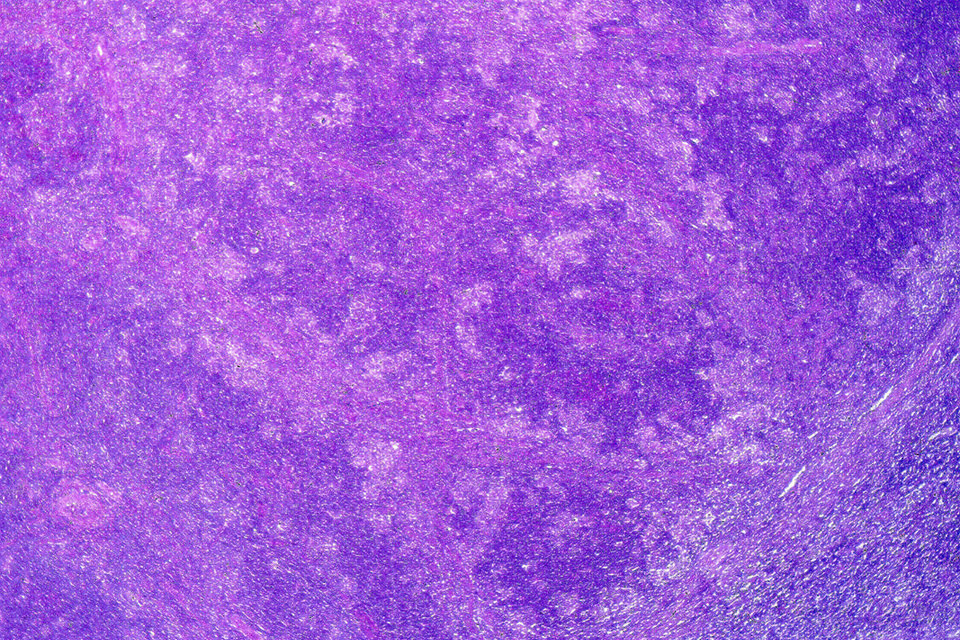
Contributed by: Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D.
Diagnosis: Nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymph node biopsy: vaguely nodular small lymphocytic proliferation (H&E, 40x).