We have posted updates of the following topics:
Autopsy & forensics > Types of injuries > Environmental deathsby Mark A. Giffen, Jr., D.O.
Topic summary: Death due to exogenous environmental factors, exposure or injury; may be due to natural phenomena, unintentional human exposure or intentional human intervention. Fire related deaths includes death due to burns, inhalation of heated gases / products of combustion or subsequent complications. Exposure to an electrical current may cause immediate death (cardiac arrhythmias) or delayed and indirect death (end organ damage, secondary blunt injuries, complications of external and internal burn injury). Hypothermia: due to environmental cold exposure overwhelming heat production. Heat related illnesses occur on a spectrum: heat edema / heat cramps; heat exhaustion; heat stroke.
Coagulation > Anticoagulants and procoagulants > 4 factor PCC
by Abdullah Alswied, M.D., Ph.D., Kathleen (Cathy) Conry-Cantilena, M.D.
Topic summary: 4 factor prothrombin complex concentrate (4F PCC) is derived from plasma pools depleted of cryoprecipitate. 4F PCC contains hemostatic levels of vitamin K dependent coagulation factors (II, VII, IX and X) and physiological amounts of coagulation inhibitory proteins, protein C and S. Brand names: Kcentra or Balfaxar. 4F PCC is indicated for the urgent reversal of acquired coagulation factor deficiency induced by vitamin K antagonist therapy in adult patients with acute major bleeding (Kcentra only) or need for an urgent surgery / invasive procedure (Kcentra and Balfaxar). Baseline and 30 minute postdose INR levels, clinical response and signs of thromboembolism during and after treatment should be monitored.
Lung > Salivary gland type tumors > Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma
by Anusmita Tripathy, M.D., Aliya N. Husain, M.D.
Topic summary: Low grade and indolent malignant neoplasm rarely seen in lung. These tumors are commonly located in the oral cavity, followed by uncommon locations, such as trachea, bronchi and nasopharynx. These tumors are identified as masses incidentally on radiological imaging and on tumor cells with demonstration of EWSR1::ATF1 gene rearrangement used as a confirmatory test. Most important differential diagnosis is squamous cell carcinoma, which also stains positively with the same immunohistochemical markers but is much more aggressive. Excellent prognosis; long term follow up may be helpful in cases having lymph node metastasis, perineural invasion and tumor necrosis, as there is limited data on the prognosis of these cases.
Nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx > Sinonasal adenocarcinoma > Nonintestinal type
by Rimlee Dutta, M.B.B.S., M.D., Rifat Mannan, M.B.B.S., M.D.
Topic summary: Malignant tumor showing glandular differentiation, with presence of intraluminal mucin (in most cases). Morphologically, lacks intestinal type features or characteristics of a salivary gland specific neoplasm; histologically divided into 2 grades: low grade (LG) and high grade (HG). Nasal obstruction is most common presenting symptom; patients harboring HG sinonasal adenocarcinoma additionally also present with epistaxis, pain, deformity and proptosis. ~25% of LG sinonasal adenocarcinoma cases recur; 6% of patients die due to tumor related morbidity; most patients of HG sinonasal adenocarcinoma die within 5 years, with evidence of local and distal metastasis. No standardized treatment; surgery followed by radiation is a mainstay in management.
Pancreas > Transplantation > Allograft rejection
by Alexei Mikhailov, M.D., Ph.D.
Topic summary: Pancreas transplant rejection is an immunological reaction directed by the host immune system against the allograft, leading to allograft damage and requiring immunosuppressive treatment to prevent permanent disruption of the allograft function. Both major and minor histocompatibility antigens activate the immune system against the allograft. Some patients with pancreas graft rejection occasionally present with mild graft tenderness or fever, whereas many patients are asymptomatic. Pancreas allograft biopsy is the gold standard in the diagnosis of pancreas rejection. Early diagnosis and successful treatment of pancreas allograft rejection results in preservation of graft endocrine function.
Featured Image
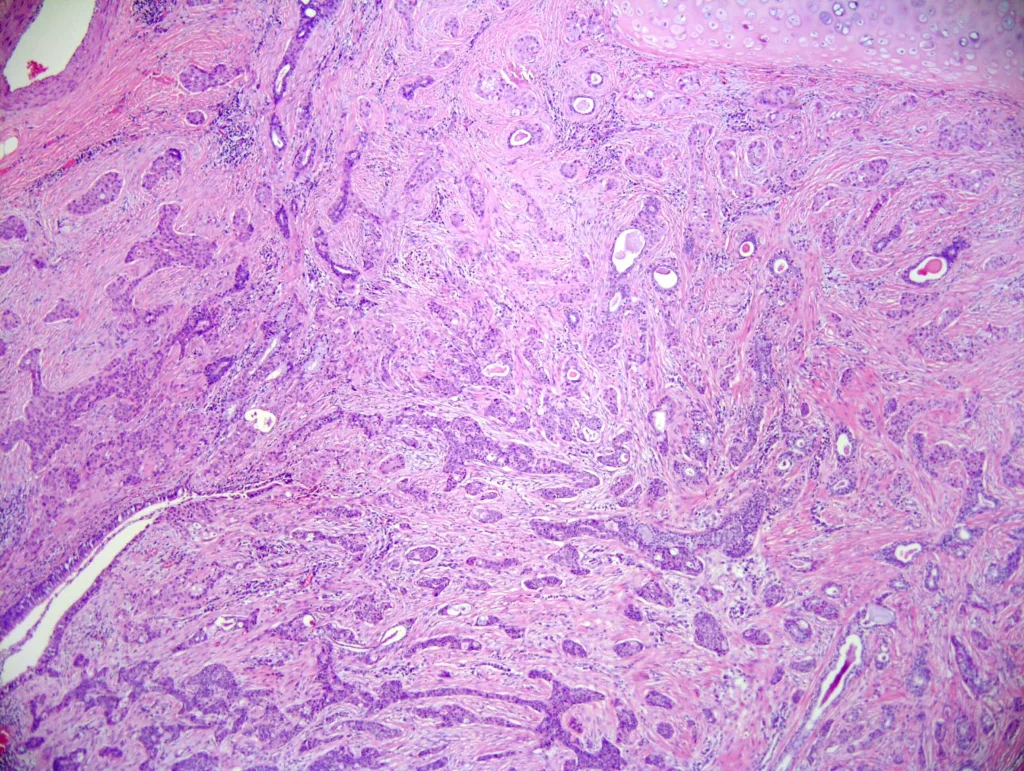
Contributed by: Aliya N. Husain, M.D.
Diagnosis: Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma
The neoplasm is arranged in nests, glands and trabeculae (H&E, 4x).