We have posted updates of the following topics:
Breast > Other nonneoplastic > Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasiaby Indu Agarwal, M.D., Luis Blanco, Jr., M.D.
Topic summary: Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH) is a benign stromal myofibroblastic proliferation forming clefts, simulating a vascular lesion. Mostly occurs in pre and perimenopausal women but can occur in males too. Myofibroblastic origin, postulated role of hormonal factors. Nonspecific findings on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ranging from an enhancing mass to clumped, nonmass-like enhancement. Nonneoplastic but mass forming lesion may rarely recur, especially in younger patients. Local excision needed only in symptomatic mass forming lesions; if diagnosed on core needle biopsy, no surgical excision is required, provided the diagnosis is concordant with radiologic findings.
Lymphoma & related disorders > Mature T/NK cell disorders > Pediatric NK/T cell disorders > Systemic EBV+ T cell lymphoma of childhood
by Michael Stone, D.O., Yoon Kyung Jeon, M.D., Carlos A. Murga-Zamalloa, M.D.
Topic summary: Often rapid and fulminant disease within the spectrum of childhood Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) positive T cell lymphomas. It occurs in pediatric and young adult immunocompetent patients and there is an overlap in symptoms, clinical outcomes, laboratory findings and histomorphological features with the other EBV+ T / NK lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood. More commonly affects people in Asia, Mexico, Central America and South America. Symptoms include hepatosplenomegaly, fever, lymphadenopathy, malaise and upper respiratory tract symptoms. Overall poor prognosis with a high mortality rate (66 – 90%). Treatment: HLH 2004 protocol or other etoposide containing regimens followed by hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Ovary > Germ cell tumors > Monodermal teratomas > Monodermal cystic teratoma
by Azin Mashayekhi, M.D., M.B.A., Gulisa Turashvili, M.D., Ph.D.
Topic summary: Benign cystic tumor of the ovary comprising mature tissues derived from a single germ layer (ectoderm or endoderm), except for struma ovarii, carcinoid and neuroectodermal type tumors. May contain pituitary type adenomas. Neuroectodermal cysts have been reported in children and young women; epidermoid cysts occur across a wide age range. Pathophysiology and etiology unknown. Clinical features: abdominal distension or pain; amenorrhea due to prolactinoma; central obesity and hirsutism due to corticotroph adenoma. Wide spectrum of radiologic presentation ranging from a purely cystic to a complex cystic mass with a considerable solid component. Benign with excellent prognosis. Treatment: cystectomy; oophorectomy.
Soft tissue > Smooth muscle > Leiomyosarcoma > Inflammatory leiomyosarcoma
by Diego M. Montoya-Cerrillo, M.D., Jaylou M. Velez-Torres, M.D.
Topic summary: Inflammatory leiomyosarcoma (ILMS) is a malignant neoplasm showing smooth muscle differentiation, a prominent inflammatory infiltrate and near haploidization. Fascicular proliferation of variably atypical eosinophilic spindle cells, which show mitotic activity (most often lymphoid or histiocytic / xanthomatous) but the composition is variable; calcospherites (psammomatous calcifications) are an uncommon and striking feature. Occurs in young to middle aged adults (30 – 40 years); male predilection. Treatment: wide local excision with negative surgical margins; radiation and chemotherapy are reserved to cases where rhabdomyosarcoma is present. When completely excised, it rarely recurs.
Stains & CD markers > Gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15)
by Joshua J.X. Li, M.B.Ch.B., Gary M. Tse, M.B.B.S.
Topic summary: A marker of apocrine differentiation; present in breast, salivary and seminal secretions with possible functions in breast carcinogenesis. Useful in confirming breast primary in metastatic carcinomas but sensitivity is lower than GATA3. Other uses: diagnosis of salivary gland carcinomas including salivary duct carcinoma and acinic cell carcinoma; differentiating primary extramammary Paget disease (positive) from secondary extramammary Paget disease (negative). Cytoplasmic staining. Gene expression profiling revealed associations between PIP gene and cell adhesion, apoptosis and proliferation in breast cancer cells. GCDFP-15 stain expression in breast cancer offers no independent prognostic value over hormone markers.
Featured Image
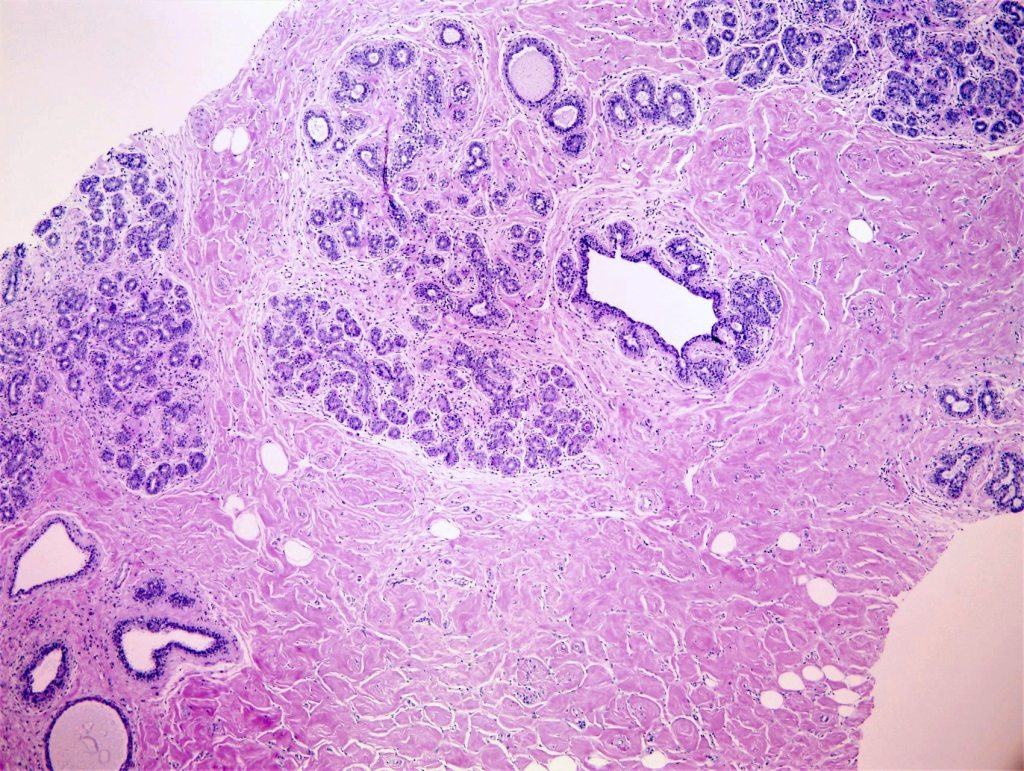
Contributed by: Indu Agarwal, M.D.
Diagnosis: Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia
Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia present in the interlobular areas of breast.